Pesquisar
ECONOMIC SITUATION:
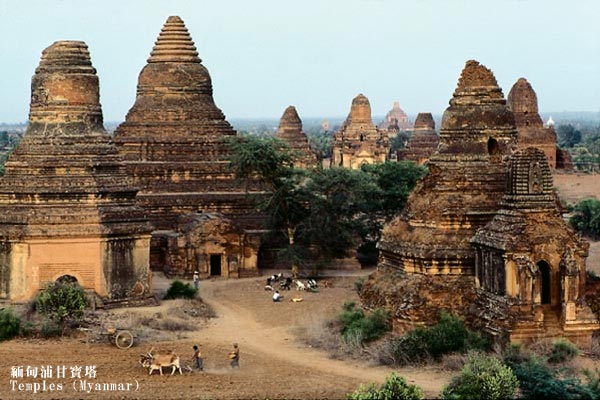
Myanmar is bordered by the People’s Republic of China to the north, Laos to the east, Thailand to the southeast, Bangladesh to the west and India to the northwest, with the Andaman Sea to the south, and the Bay of Bengal to the southwest. Myanmar is rich in natural resources, but over the years, economic development has slowed In recent years, the government has pursued market-orientated economic policies, including the development of private enterprises and attracting foreign investment.
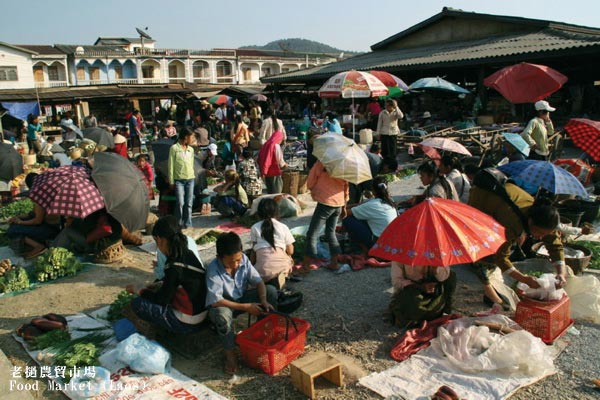
Laos is bordered by Myanmar (Burma) and the People’s Republic of China to the northwest, Vietnam to the east, Cambodia to the south, and Thailand to the west. The main economic activity is agriculture, which has was weakened during the civil war, which ended in 1975 and has never fully recovered. In 1988, liberal reforms were implemented, the economic structure was modulated, which incorporated the farming and forestry industry, manufacturing and services, in which the development of farming and forestry was given top priority, revoking the high degree of concentration system of economic management. This in turn encouraged diversified forms of economic strategies, gradually consummating market-orientated economic policies and striving to transfer the natural economy and semi- natural economy to a market-orientated economy; including the welcoming of foreign investors, promulgating foreign capital law, improving the investment environment; widening foreign economic relations and striving to attract more foreign investment, advanced technology and management methods. Please look at this as it isn’t too clear.
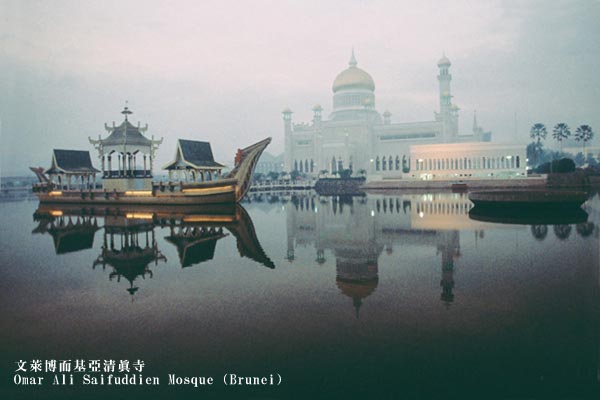
Brunei is located on the island of Borneo, in Southeast Asia. Apart from its coastline on the South China Sea, it is completely surrounded by the East Malaysian states of Sarawak and Sabah. Brunei is one of the main crude oil producers in Southeast Asia and it is one of the world’s major producers of natural gas. Crude oil and natural gas supports the national economy, which accounts for 40%of its GDP and 88% of its total exports. In recent years, the development of crude oil products, a port extension and the construction of other infrastructure has attracted foreign investment and promoted economic diversification.
BUSINESS OPPORTUNITIES:
MYANMAR (BURMA)

Agro-based industries
The policy of the Government is to promote the development of agro-based industries along with the increased production of agricultural commodities. Under MOAI, several industries such as jute, sugar, cotton, sericulture, pesticides, rubber, farm machinery and tools plus a canning factory are being operated. At present, those interested in setting up new industries or upgrading existing ones are welcome and MOAI is encouraging private investors to establish plantations and suitable agro-based industries.
Hotels and Tourism
Another sector with bright prospects is tourism. Myanmar is a cultural destination with its rich cultural heritage and it is also blessed with snow-capped mountains, beautiful lakes, rivers lush tropical forests, unspoilt beaches and archipelagos for environmental tourists. There is a growing need for international class hotels in major tourist sites. There are also many newly opened areas where there are no top class hotels. Many opportunities for investment in developing golf courses, beach resorts, tourist villages, amusement parks, recreational centres are also available.
LAOS

Textiles
Lao PDR has made a name for itself around the world as both a location as a cost-effective manufacturer of garments and high-end woven fabrics. The primary markets for the wholesale distribution of Lao garments are Thailand and Europe. Lao products enter the EU duty-free due to its status in the Quota-Free Generalised Preferential System. When the Asian Art Museum in San Francisco re-opened in March 2003, among the most costly items in its gift shop were Lao textiles. Demand for quality fabrics remains very high, and the overseas market is largely untapped.
Telecommunications
The percentage of the Lao population with a telephone service is low (less than 2%) but it is increasing. There is a great need for telecommunications infrastructure and recent investors have seen a rapid increase in the mobile phone network. Whilst there are now four telephone companies in the country, there remains a need for increased investment in the national infrastructure. The government is especially keen to see the network extended to the rural and remote areas. Other servers are at various stages of development or applying for business licenses.
BRUNEI

Manufacturing
The manufacturing sector currently plays a relatively minor role in Brunei’s economy, accounting for 3.9% of GDP. The government has identified manufacturing as an important area for economic diversification. While Brunei already manufactures a number of products for export – including construction materials, electrical products and furniture – the garment industry is recording the fastest growth.
Agriculture, forestry and fisheries
Currently, the agricultural sector contributed 2.8% to the total GDP. Brunei imports a significant amount of food for domestic consumption. A notable success story in the agricultural sector is the harvesting of vegetables, which has risen by over 100% over the last 10 years, recording an estimated annual harvest of 10,360 metric tonnes. The government has estimated the fisheries industry has a potential value of some BND$200 million per year. Despite this, Brunei’s current consumption of fish is predominantly import-dependent.
MAJOR WEBSITE RECOMMENDATION:
- MYANMAR GOVERNMENT WEBSITE
http://www.myanmar.com
The Myanmar Government Website is a formal website that publishes reliable information about the country’s policies, laws, government decisions and social economic development in Myanmar. - LAOS NATIONAL ASSEMBLY WEBSITE
http://www.na.gov.la
The Laos National Assembly Website is a for mal website that publishes reliable information about the country’s policies, laws, government decisions and social economic development in Laos. - BRUNEI GOVERNMENT WEBSITE
http://www.brunei.gov.bn
The Brunei Government Website is a formal website that publishes reliable information about the country’s policies, laws, government decisions and social economic development in Brunei.
Source:
Myanmar
http://www.myanmar.gov.mm/ministry/agri/business.htm
http://www.myanmar-embassy-seoul.com/trade.html
Laos
http://www.invest.laopdr.org/business%20guide.htm
Brunei
http://www.dfait-maeci.gc.ca/brunei/business-en.asp
|
MYANMAR – MAIN ECONOMIC INDICATORS 2006
|
|
| Gross Domestic Product (US$ Billions) | 9.6 |
| Real GDP growth (%) | 2.6 |
| GDP per capita (current US$) | 1,800 |
| Inflation (%) | 21.4 |
| Land area (ten thousand sq km) | 67.9 |
| Population (Million) | 47.4 |
| Exports (US$ Billions) | 3.56 |
| Imports (US$ Billions) | 1.98 |
| Main Exports – commodities: Commodities: Gas, Wood Products, Pulses and Beans, Fish | |
| Main Imports – commodities: Commodities: Fabric, Petroleum Products, Fertiliser, Plastics | |
| Main Exports – commodities (2005): Thailand, India, China, Japan | |
| Main Imports – commodities (2005): China, Thailand, Singapore, Malaysia | |
Source: CIA- The World Fact Book-Myanmar https://www.cia.gov/cia/publications/factbook/geos/bm.html
|
LAOS – MAIN ECONOMIC INDICATORS 2006
|
|
| Gross Domestic Product (US$ Billions) | 2.8 |
| Real GDP growth (%) | 7.2 |
| GDP per capita (current US$) | 2,100 |
| Inflation (%) | 6.8 |
| Land area (ten thousand sq km) | 23.7 |
| Population (Million) | 6.4 |
| Exports (US$ Billions) | 982.2 |
| Imports (US$ Billions) | 1.4 |
| Main Exports – commodities: Garments, Wood Products, Coffee, Electricity Appliances | |
| Main Imports – commodities: Machinery and Equipment, Vehicles, Fuel, Consumer Goods | |
| Main Exports – commodities (2005): Thailand, Vietnam, France, Germany | |
| Main Imports – commodities (2005): Thailand, China, Vietnam | |
Source: CIA- The World Fact Book-Laos https://www.cia.gov/cia/publications/factbook/geos/la.html
|
BRUNEI – MAIN ECONOMIC INDICATORS 2006
|
|
| Gross Domestic Product (US$ Billions) | 9.5 |
| Real GDP growth (%) | 0.4 |
| GDP per capita (current US$) | 25,600 |
| Inflation (%) | 1.1 |
| Land area (ten thousand sq km) | 0.6 |
| Population (Million) | 0.4 |
| Exports (US$ Billions) | 6.2 |
| Imports (US$ Billions) | 1.5 |
| Main Exports – commodities: Crude Oil, Gas, Refined Products, Clothing | |
| Main Imports – commodities: machinery and transport equipment, manufactured goods, food, chemicals | |
| Main Exports – commodities (2005): Japan, Indonesia, South Korea, US | |
| Main Imports – commodities (2005): Singapore, Malaysia, Japan, UK | |
Source: CIA- The World Fact Book-Brunei https://www.cia.gov/cia/publications/factbook/geos/bx.html
|
MAINLAND CHINA – MYANMAR BILATERAL TRADE (Unit: Million US$)
|
|||
|
Year
|
Total Trade
|
Exports
|
Imports
|
|
2006
|
146,007
|
120,742
|
25,265
|
|
2005
|
120,933
|
93,493
|
27,440
|
|
2004
|
114,549
|
93,859
|
20,690
|
|
2003
|
107,725
|
90,771
|
16,953
|
|
2002
|
86,171
|
72,482
|
13,689
|
|
MAINLAND CHINA – LAOS BILATERAL TRADE (Unit: Million US$)
|
|||
|
Year
|
Total Trade
|
Exports
|
Imports
|
|
2006
|
21,836
|
16,872
|
4,965
|
|
2005
|
12,892
|
10,338
|
2,555
|
|
2004
|
29,895
|
4,789
|
25,106
|
|
2003
|
10,944
|
9,824
|
1,120
|
|
2002
|
6,395
|
5,431
|
965
|
|
MAINLAND CHINA – BRUNEI BILATERAL TRADE (Unit: Million US$)
|
|||
|
Year
|
Total Trade
|
Exports
|
Imports
|
|
2006
|
31,494
|
9,963
|
21,531
|
|
2005
|
26,087
|
5,314
|
20,773
|
|
2004
|
11,354
|
10,088
|
1,265
|
|
2003
|
34,617
|
3,389
|
31,228
|
|
2002
|
26,297
|
2,106
|
24,181
|
Source: Ministry of Commerce of the People Republic of China http://zhs.mofcom.gov.cn/tongji.shtml
|
MACAO – MYANMAR BILATERAL TRADE – MAIN CATEGORIES AND PRODUCTS IN 2006
|
||
|
Category
|
Weight (KG)
|
MOP
|
|
Imports
|
44,567
|
1,136,920
|
|
Exports
|
1,750
|
104,538
|
|
Re-exports
|
1,750
|
104,538
|
|
Transit
|
270
|
132,382
|
|
MACAO – LAOS BILATERAL TRADE – MAIN CATEGORIES AND PRODUCTS IN 2006
|
||
|
Category
|
Weight (KG)
|
MOP
|
|
Imports
|
35
|
43,142
|
|
Exports
|
–
|
–
|
|
Re-exports
|
–
|
–
|
|
Transit
|
–
|
–
|
Note 1 : Exports = Domestic Exports + Re-exports
Note 2 : From May 2000, data on Transit is only available up to the 4th digit of NCEM/HS
SOURCE:
- The Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the People’s Republic of China
http://www.fmprc.gov.cn/chn/ - The Ministry of Commerce of the People’s Republic of China
http://www.mofcom.gov.cn/ - The Embassy of the People’s Republic of China in the Union of Myanmar
http://wcm.fmprc.gov.cn/ce/cemm/chn/ - The Embassy of the People’s Republic of China in Negara Brunei Darussalam
http://bn.china-embassy.org/chn/default.htm - The Economic and Commercial Counsellor’s office of the Embassy of the People’s Republic of China in Myanmar
http://big5.mofcom.gov.cn/gate/big5/mm.mofcom.gov.cn/index.shtml - The Economic and Commercial Counsellor’s office of the Embassy of the People’s Republic of China in the People’s Democratic Republic of Laos
http://la.mofcom.gov.cn/index.shtml - The Economic and Commercial Counsellor’s office of the Embassy of the People’s Republic of China in Negara Brunei Darussalam
http://bn.mofcom.gov.cn/index.shtml - Macao Statistics and Census Service
http://www.dsec.gov.mo/c_index.html - Macao Economic Services
http://www.economia.gov.mo/ - Macao Trade and Investment Promotion Institute
http://www.ipim.gov.mo/pt-pt/ - Myanmar Government Website
http://www.myanmar.com - Laos Government Website
http://www.na.gov.la - Brunei Government Website
http://www.brunei.gov.bn