Search Issues
The People’s Republic of Bangladesh
Basic Information
The People’s Republic of Bangladesh (hereinafter referred to as “Bangladesh”) is located on the delta formed by the confluence of the Ganges and Brahmaputra River in the north-eastern part of the South Asian subcontinent, bordering India to the east, west and north, Myanmar to the southeast and Bay of Bengal to the south. With a coastline of 550 kilometres and a land area of 147,570 square kilometres, the country is divided into seven administrative regions: Dhaka, Chittagong, Khulna, Rajshahi, Barishal, Sylhet and Rangpur. With over 20 ethnic minorities, Bangladesh has a population of more than 160 million, of which 98% are Bengalis. The main religion is Islam. Bengali is the national language and English is the official language. Dhaka is the not only the capital and largest city of Bangladesh, but also the political, economic and cultural centre of the country, as well as one South Asia’s major cities.
Bangladesh is one of the least developed countries at an economic level; its national economy mainly depends on agriculture. International aid is an important source of Bangladesh’s foreign exchange reserves and a major source of funds for its investment and development projects. In recent years, the Bangladesh government has advocated a market economy, improved the investment environment, increased efforts to attract foreign investment and formulated a huge economic development plan, including the building of a “digital Bangladesh”, increasing power generation capacity and achieving food self-sufficiency. However, it faces challenges such as shortage of funds, technology and energy. Bangladesh has trade relations with more than 130 countries and regions. The main export markets are the United States, Germany, the United Kingdom, Spain and France. The main export products include jute and related products, leather, tea, aquatic products and clothing. In terms of imports, the main sources are China, India, the United States and Japan. The main imported commodities include textiles, petroleum and related products, edible oil, cotton, steel and other base metals. Currently, Bangladesh is a member of the United Nations (UN), Indian Ocean Rim Alliance (IORA), Organisation of Islamic Co-operation (OIC), Commonwealth of Nations and other international organisations.
Economic and trade co-operation between China and Bangladesh
Since the establishment of diplomatic relations in 1975, Bangladesh and China have maintained friendly and co-operative relations, with frequent high-level exchanges and fruitful collaboration in political, economic, military, cultural and other fields. Besides, the two countries share basically the same views on a series of major international and regional issues and work closely in international affairs. In 2014, the two countries announced the “Joint Statement on Deepening the Closer Comprehensive Partnership of Co-operation between Bangladesh and China”, which in 2016, was upgraded to a strategic co-operative partnership, in order to further strengthen the collaboration and relationship to a new level.
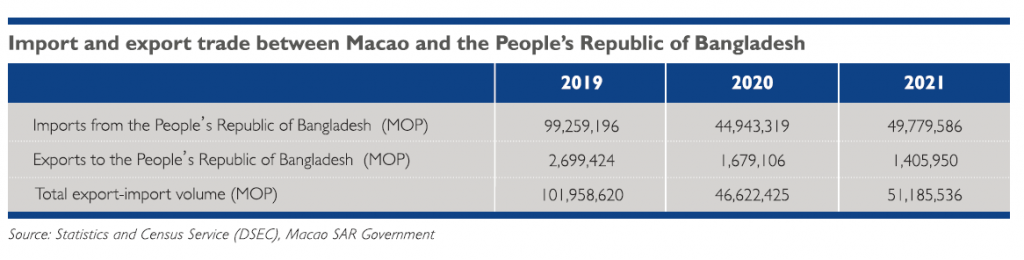
Regarding economic and trade co-operation, in 1983, Bangladesh and China established a joint committee on economy, trade and science and technology. In addition, the two sides have signed a number of agreements for the economic and technical co-operation, encouragement and protection of investments, avoidance of double taxation and prevention of tax evasion. China is the largest source of Bangladesh’s imports, which mainly imports textiles, mechanical and electrical products, cement, fertilizers, tires, raw silk, corn and other commodities from China, and exports raw materials such as leather, cotton textile products and fish to China. In terms of investment, Bangladesh is not only one of China’s major recipient countries, but also a traditional market of China’s foreign contracting projects in South Asia.
In terms of cultural and educational collaboration, Bangladesh and China have signed an agreement on cultural co-operation between the two governments. The two countries have been sending students to each other since 1976. China established in Bangladesh a Confucius Institute at North South University in 2006 and a Confucius Classroom at Shanto-Mariam University in 2009. In terms of tourism collaboration, a direct flight between Beijing and Dhaka was launched in May 2005. After that, Kunming and Chittagong established a sister-city relationship.
Business opportunity information of Bangladesh
Bangladesh’s mineral resources are relatively limited, with declared reserves of natural gas of 311.39 billion cubic metres, coal reserves of 750 million tons. The forest area of Bangladesh is about 2 million hectares, covering 13.4% of the country.
In terms of industry, Bangladesh is dominated by the raw material industry, including cement, fertilizer, jute and its products, sugar, cotton yarn, soybean oil and paper. The heavy industry of the country is weak and its manufacturing industry is underdeveloped.
In relation to the airline industry, Biman Bangladesh operates three domestic routes and 18 international routes. At present, Bangladesh has three international airports, located in Dhaka, Chittagong and Sylhet, with direct flights between Dhaka and Guangzhou, Kunming and Hong Kong.