Search Issues
The United Arab Emirates
Basic Info
The United Arab Emirates, commonly known as the Emirates, is formed from a federation of seven emirates, consisting of Abu Dhabi, Ajman, Dubai, Fujairah, Ras Al Khaimah, Sharjah, and Umm Al Quwain. The UAE is located in the south-east of the Arabian Peninsula in south-west Asia, sharing borders with Oman and Saudi Arabia. It has an area of 83,600 square kilometres and a population of over 9.8 million, of whom 88.5% are expatriates, mainly from India, Pakistan, Egypt, Syria, Palestine and other countries. The majority of the population is Islamic and the official language is Arabic, with English being the common language. Abu Dhabi, the capital of the United Arab Emirates, has been actively developing its tourism industry in addition to its oil industry.
The UAE ranked the 34th in the world with a GDP of US$358.9 billion in 2020. The economy is dominated by oil production and petrochemical industries. In order to promote a diversified economy, the UAE has made a lot of effort in recent years to expand trade and increase non-oil revenues, and to develop industries such as cement, aluminium, plastic products, construction materials, garments and food processing. At the same time, the UAE has also focused on the development of agriculture, livestock, fisheries, culture, education and health services, as well as a knowledge-based economy with information technology at its core. The UAE is currently a member of the United Nations (UN), the World Trade Organisation (WTO), the Organisation of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC), the Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA), the Organisation for Islamic Co-operation (OIC) and the League of Arab States, among other international organisations.
Overview of Economic and Trade Co-operation between China and the United Arab Emirates
China and the UAE formally established diplomatic relations in 1984. Since the establishment of diplomatic relations, the two countries have enjoyed a smooth development of friendship and co-operation, with frequent high-level visits to each other and mutual support and co-operation in international and regional affairs. In January 2012, China and the UAE established a strategic partnership. In December 2017, the two countries reached an agreement on mutual visa-free access for ordinary passport holders, which officially came into effect on 16 January 2018. Subsequently, in July 2018, the two sides established a comprehensive strategic partnership and signed a memorandum of understanding on the “Belt and Road Initiative”, and reached an agreement on founding cultural centres for each other, further taking the collaboration and relationship between the two countries to a new level.
In terms of medical and public health, in June 2020, China National Pharmaceutical Group and the UAE collaborated to launch the world’s first phase III international clinical trial of an inactivated vaccine against COVID-19 in the UAE. In March 2021, China and the UAE launched a project on the production line for the filling of vaccine stock in both countries. In July 2021, China, the UAE and Serbia signed the “Memorandum of understanding on co-operation in the production of COVID-19 vaccine”.
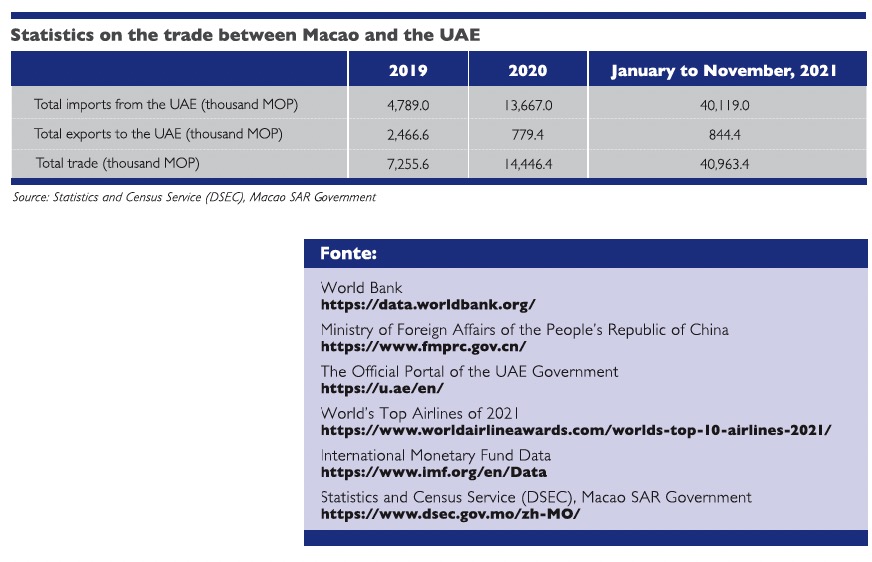
In terms of economic and trade reciprocation, the UAE is China’s largest export market and second largest trading partner in the Arab world. China mainly exports electrical and mechanical equipment, high technology, textiles and light industrial products to the UAE, and mainly imports liquefied petroleum gas, crude oil, refined oil products, aluminium and aluminium products from the UAE.
Information of Business Opportunities
The United Arab Emirates is rich in oil and natural gas resources, with proven oil reserves of approximately 15 billion tonnes and natural gas reserves of approximately 7.7 trillion cubic metres, both of which rank sixth in the world. In terms of industry, the petrochemical industry is the mainstay, while various industries such as natural gas liquefaction, aluminium refining, plastic products and construction materials are also actively developed.
The UAE’s agriculture sector is underdeveloped, with a small livestock industry, while fishery products meet domestic demand. The country depends on imports for food. To encourage the development of the agricultural policy, the government provides free seeds, chemical fertilisers and interest-free loans to farmers, and underwrites the purchase and sale of agricultural products to ensure farmers’ income.
In terms of transport, there are 39 airports in the UAE, including seven international airports such as Abu Dhabi and Dubai. The Emirates Airline is ranked 4th in the world according to the World’s Best Airlines 2021 survey by Skytrax, a global airline research firm. In addition, the UAE has 12 major seaports, including Jebel Ali Port in Dubai, the world’s largest man-made port and the largest port in the Middle East.
In terms of finance, the federal government’s revenue comes mainly from the oil and trade revenues of the various Emirates. The UAE’s banking sector is also very well developed, with unrestricted foreign exchange, free currency entry and exit and stable exchange rates. External trade plays an important part in the UAE economy. The main exports are oil, gas, petrochemicals and aluminium ingots and the main imports are food, machinery and consumer goods.